Operating Margin: What It Is and the Formula for Calculating It, With Examples

A poor management team could post a strong operating ratio in one year by cutting valuable investments in areas like R&D, marketing, or maintenance capex. This would hurt the company’s competitive position over the long run, even if it boosted the operating Ratio in the short term. Similarly, firms with strong brands or competitive advantages could post higher operating margins than the operating Ratio would suggest.
What is the Operating Ratio Formula?
It is arrived at by dividing the sum of operating expenses and the cost of goods sold by the net sales. Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy.
What are the uses of operating ratios?
Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. We will use the following sample financial statements as the example for all of our ratios. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
A Healthy Operating Profit Margin Defined
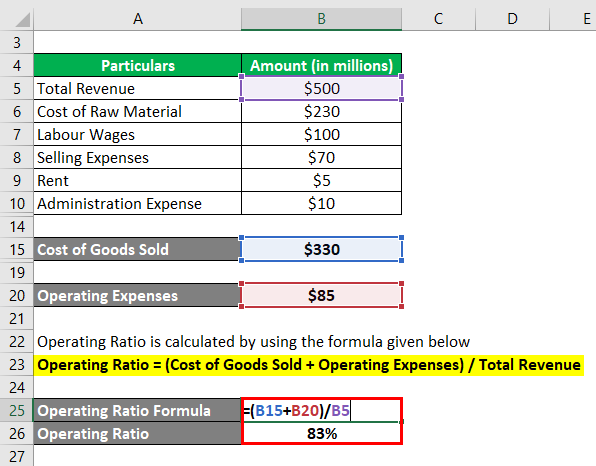
- Operating expenses include the cost of goods sold, selling, general and administrative expenses, depreciation, and other operating expenditures.
- There are five scenarios where an operating ratio over 100% arises for a public company whose stock is traded on exchanges.
- Choose CFI for unparalleled industry expertise and hands-on learning that prepares you for real-world success.
- A constant operating ratio means this metric persists at roughly the same level year after year rather than fluctuating widely.
Analysts look at operating ratios over several time periods to spot trends. Comparing current ratios to historical norms also offers perspective on how efficiently the company is running. Using consistent time periods, such as the last twelve months, allows for reliable apples-to-apples comparisons. A company may need to implement cost controls for margin improvement if its operating ratio increases over time.
Is operating Ratio necessary for financial ratio analysis?
“Before a company can prosper in the long term, it must first be able to survive in the short term,” wrote Investopedia. Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their when does your child have to file a tax return best advice on how to take your company to the next level. Boosting sales, however, often involves spending more money to do so, which equals greater costs.
Operating ratio is referred to as the ratio that depicts the efficiency of the management by establishing a relationship between the total operating expenses with the net sales. EBITDA is sometimes used as a proxy for operating cash flow because it excludes non-cash expenses, such as depreciation. This is because it does not adjust for any increase in working capital or account for capital expenditure that is needed to support production and maintain a company’s asset base—as operating cash flow does. For stock investors, this decreasing ability to convert revenue into profit is a worrisome sign.
The lower the Ratio, the better it is for the company, as it indicates the company is spending less to generate each rupee of revenue. The operating ratio compares production and administrative expenses to net sales. A low ratio in comparison to that of competitors indicates that management is doing a good job of keeping costs in line. The operating ratio indicates little when taken as a single measure for one time period, since operating expenses can vary considerably between months. If sales are seasonal, it can make sense to compare a month’s results to those of the same month in the preceding year.
Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
The operating margin is an important measure of a company’s overall profitability from operations. It is the ratio of operating profits to revenues for a company or business segment. When calculating operating margin, the numerator uses a firm’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). EBIT, or operating earnings, is calculated simply as revenue minus cost of goods sold (COGS) and the regular selling, general, and administrative costs of running a business, excluding interest and taxes. Digging deeper into the key drivers behind changes in the operating Ratio provides color into what business factors are impacting costs and margins. For example, is an increasing operating ratio being driven by rising input costs, labor cost inflation, excess capacity, or ineffective price management?
One of the most basic uses of the operating Ratio is gauging profitability. By dividing operating expenses by revenue, the Ratio quantifies what proportion of revenue is left over after operating costs are covered. A low ratio indicates a high-margin business with room to pay expenses like interest and taxes and still deliver profits. Comparing operating ratios over time shows if margins are expanding or shrinking. Office supply expenses, while essential for business operations, diminish operating profitability ratios weighed by stock market analysts judging a company’s expense discipline and working capital management. Analysts use trends in a company’s operating Ratio over multiple years to evaluate how well management is controlling costs as revenues grow.
For example, grocery stores typically have low margins and high operating ratios, while software companies have higher margins and lower operating ratios. Comparing the operating ratios of companies in different sectors does not provide an accurate benchmark. Operating ratio is an important financial metric used to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of a company. The operating Ratio measures how much it costs a company to generate each rupee of revenue.
